Weapon System Sustainment: DOD Identified Operating and Support Cost Growth but Needs to Improve the Consistency and Completeness of Information to Congress
Fast Facts
DOD spends billions of dollars a year to operate and maintain its weapon systems. These "sustainment" costs—such as for repair parts or personnel—account for about 70% of a weapon system's total cost. DOD reports to Congress on these costs annually.
We looked at DOD's FY 2022 sustainment reviews, and found that 7 out of 16 weapon systems had sustainment cost growth above the thresholds identified in law. We also found that the military services vary in how they report cost details—such as the effects of inflation. Consistently reporting cost information would improve oversight.
We recommended that DOD address this issue.
The DOD reports on weapons system sustainment costs annually, such as those for the Navy’s EA-18G Growler plane

Highlights
What GAO Found
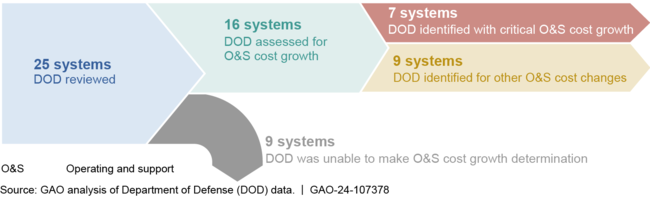
The Department of Defense (DOD) conducted sustainment reviews for 25 weapon systems for fiscal year 2022, including developing operating and support (O&S) cost estimates for the remainder of each system's life cycle. O&S costs are comprised of costs for repair parts, maintenance activities, contract services, and personnel. DOD assessed O&S cost growth for 16 systems but was unable to make cost growth determinations for the nine remaining systems, due to a lack of available information to conduct the comparison (see first figure). DOD identified critical cost growth for seven of the 16 systems and the reasons for that growth (see second figure). A statute defines critical O&S cost growth as at least 25 percent more than the estimate documented in the most recent independent cost estimate; or at least 50 percent more than the estimate documented in the original baseline cost estimate for the system. The other nine systems experienced O&S cost changes, but any growth identified did not meet the critical O&S cost growth criteria.
Number of Weapon Systems Reviewed and Operating and Support (O&S) Cost Growth Identified by the Department of Defense (DOD) in Fiscal Year 2022
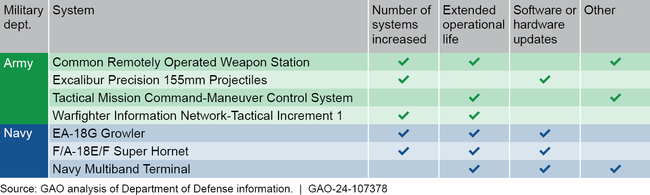
Causes of Critical Operating and Support (O&S) Cost Growth in Seven Systems
DOD's Office of Cost Assessment and Program Evaluation updated its guidance based on lessons learned from the most recent sustainment reviews. However, military departments vary in how they report the details of cost estimates. For example, they presented cost information differently in several areas, including the time frames for the estimate, the breakdown of information across cost categories, and the effects of inflation. Without the development and implementation of clear guidance on the presentation of such information, DOD stakeholders and Congress will not have consistent and complete information for effective decision making and oversight.
Why GAO Did This Study
DOD spends billions of dollars to sustain its weapon systems. O&S costs are about 70 percent of a system's total life-cycle cost. In response to a statutory provision, DOD is required to annually submit sustainment reviews that include O&S cost estimates and the reasons for any critical cost growth.
The William M. (Mac) Thornberry National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2021 included a provision for GAO to review DOD's annual sustainment reviews and O&S cost estimates through 2025. GAO's report evaluates the extent to which DOD (1) developed sustainment reviews for fiscal year 2022 that identified critical O&S cost growth and related causes; and (2) identified and implemented any lessons learned for critical O&S cost growth from conducting the reviews.
GAO reviewed and analyzed DOD guidance and documentation, the submitted fiscal year 2022 reviews, and the supporting independent cost estimates. GAO interviewed DOD officials who conducted the reviews. This is a public version of a sensitive report that GAO is issuing concurrently. GAO omitted information that DOD deemed sensitive.
Recommendations
GAO is recommending that DOD implement clarifying guidance for sustainment review submissions to ensure that the military departments are consistently presenting cost information, such as the time frame of the cost estimate, the cost categories, and the effects of inflation. DOD agreed with the recommendation.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should ensure the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment, in coordination with CAPE and the military departments, develops and implements clarifying guidance about what independent cost estimate information to include in the sustainment review submissions to the congressional defense committees to ensure the military departments are consistently presenting sunk costs, the time frames for the independent cost estimates, the cost categories, and the effects of inflation in their critical O&S cost growth information. (Recommendation 1) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
