Biodefense: National Biosurveillance Integration Center Has Taken Steps to Address Challenges, but Could Better Assess Results
Fast Facts
The Department of Homeland Security's National Biosurveillance Integration Center identifies and tracks biological events—such as avian flu—from thousands of data sources. This data helps to provide early warning and situational awareness about biological events to federal, state, and other partners.
NBIC has been working to address data access and other challenges. But several milestones in its strategic plans are broad and there aren't clear timeframes for accomplishing them. For example, one milestone is to strengthen relationships with relevant DHS offices, but it doesn't detail how it would do so. We recommended addressing this.
NBIC monitors biological events such as the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza

Highlights
What GAO Found
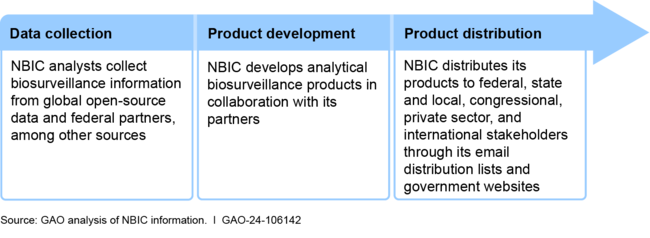
The National Biosurveillance Integration Center (NBIC), within the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), identifies, tracks, and characterizes biological events using open-source, federal, and private sector data sources. NBIC integrates these data to develop written products and support its information sharing and coordination activities.
National Biosurveillance Integration Center (NBIC) Product Development and Distribution Process, as of October 2023:
In addition, in recent years, NBIC began taking steps to address challenges in accessing needed data, obtaining adequate personnel, and developing new technologies. NBIC's efforts were guided by two strategic planning documents. But these documents did not have clearly defined performance measures and time frames for accomplishing milestones. For example, one milestone is to strengthen relationships with relevant DHS components but no additional details were included. By developing clearly defined performance measures, NBIC could better assess program results and share this information with DHS management and federal stakeholders.
NBIC evaluates the quality and reach of its products and the federal stakeholders GAO interviewed reported generally favorable views of its written products. The stakeholders included those that were familiar with NBIC's principal written products or who had participated in NBIC's coordination and information sharing activities. Officials from 11 of 12 federal agencies and two national public health associations told GAO that they use NBIC products, along with other sources, to help inform their situational awareness of global biological events.
NBIC incorporated COVID-19 related information into its existing products and conducted some original analyses to support DHS management throughout the pandemic. These analyses included monitoring cross border health trends and global flight patterns. According to NBIC officials, they have produced thousands of COVID-related products since January 2020. Several of NBIC's federal stakeholders told GAO that NBIC's products were particularly helpful during the early stages of the pandemic when information about the disease was limited.
Why GAO Did This Study
Biosurveillance is the process of gathering, interpreting, and communicating information to provide early warning and situational awareness about biological events. The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated that biological events can cause massive health, social, and economic disruption. It also underscored the importance of developing and maintaining a national biosurveillance capability.
Statute directs NBIC to consolidate information from human health, animal, plant, food, and environmental monitoring systems across the federal government to improve the likelihood of identifying a biological event at an early stage.
GAO was asked to evaluate NBIC program activities. This report discusses (1) how NBIC collects and integrates biosurveillance data, addresses related challenges, and assesses its performance; (2) the extent to which NBIC evaluates its products and obtains feedback from stakeholders; and (3) NBIC's role during the COVID-19 pandemic. To conduct this work, GAO reviewed NBIC products and related agency documentation, interviewed NBIC officials and a selection of stakeholders from 12 federal agencies and two national associations, and analyzed NBIC's strategic planning documents.
Recommendations
GAO is recommending that DHS ensure that NBIC develops future strategic planning documents with clearly defined performance measures and associated time frames. DHS concurred with this recommendation.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Countering Weapons of Mass Destruction Office | The Assistant Secretary for CWMD should ensure that NBIC's future strategic planning documents contain clearly defined performance measures with associated time frames so that they can be used to assess program results and communicate this information to management and stakeholders. (Recommendation 1) |
As of February 2024, DHS reported that the National Biosurveillance Integration Center is on track to finalize both the strategy and implementation plan by September 30, 2024.
|
