Financial Audit: FY 2022 and FY 2021 Consolidated Financial Statements of the U.S. Government
Fast Facts
The Financial Report of the U.S. Government provides a comprehensive view of government finances, including revenues, costs, assets, liabilities, and long-term sustainability.
We audit the financial statements in that report each year, but we haven't yet been able to determine if they are fairly presented. This year, it was primarily due to:
- Serious financial management problems at the Department of Defense
- Unresolved differences in balances between federal agencies
- Weaknesses in the process for preparing the statements
- Inadequate support for the cost of Small Business Administration and Department of Education loan programs
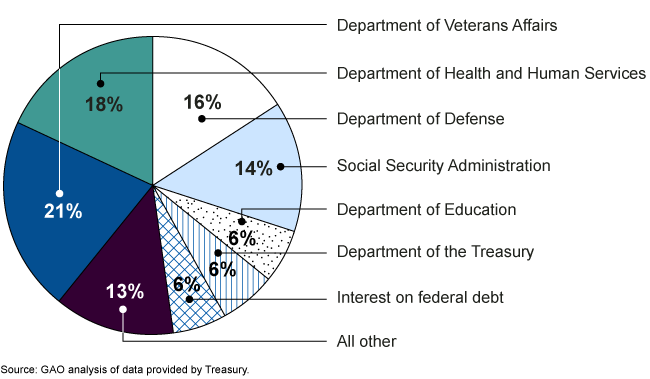
FY 2022 Net Costs of the U.S. Government Operations ($9.1 trillion)
Highlights
What GAO Found
To operate as effectively and efficiently as possible, Congress, the administration, and federal managers must have ready access to reliable and complete financial and performance information—both for individual federal entities and for the federal government as a whole. GAO's report on the U.S. government's consolidated financial statements for fiscal years 2022 and 2021 discusses progress that has been made, but also underscores that much work remains to improve federal financial management and that the federal government continues to face an unsustainable long-term fiscal path.
GAO found the following:
- Certain material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting and other limitations resulted in conditions that prevented GAO from expressing an opinion on the accrual-based consolidated financial statements as of and for the fiscal years ended September 30, 2022, and 2021.
- Significant uncertainties, primarily related to the achievement of projected reductions in Medicare cost growth, prevented GAO from expressing an opinion on the sustainability financial statements, which consist of the 2022 and 2021 Statements of Long-Term Fiscal Projections; the 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019, and 2018 Statements of Social Insurance; and the 2022 and 2021 Statements of Changes in Social Insurance Amounts. A material weakness in internal control also prevented GAO from expressing an opinion on the 2022 and 2021 Statements of Long-Term Fiscal Projections.
- Material weaknesses resulted in ineffective internal control over financial reporting for fiscal year 2022.
- Material weaknesses and other scope limitations, discussed above, limited tests of compliance with selected provisions of applicable laws, regulations, contracts, and grant agreements for fiscal year 2022.
Three major impediments have continued to prevent GAO from rendering an opinion on the federal government's accrual-based consolidated financial statements: (1) serious financial management problems at the Department of Defense, (2) the federal government's inability to adequately account for intragovernmental activity and balances between federal entities, and (3) weaknesses in the federal government's process for preparing the consolidated financial statements. In addition, the Small Business Administration (SBA) was unable to obtain an opinion on its fiscal years 2020 through 2022 financial statements and the Department of Education was unable to obtain an opinion on its fiscal year 2022 financial statements, because of weaknesses related to loans and loan guarantees. Efforts are under way to resolve these issues.
The material weaknesses underlying these three major impediments, as well as the weaknesses identified at SBA and Education, (1) hamper the federal government's ability to reliably report a significant portion of its assets, liabilities, costs, and other related information; (2) affect the federal government's ability to reliably measure the full cost, as well as the financial and nonfinancial performance, of certain programs and activities; (3) impair the federal government's ability to adequately safeguard significant assets and properly record various transactions; and (4) hinder the federal government from having reliable, useful, and timely financial information to operate effectively and efficiently.
Two other continuing material weaknesses are the federal government’s inability to (1) determine the full extent to which improper payments occur and reasonably assure that appropriate actions are taken to reduce them and (2) identify and resolve information system control deficiencies and manage information security risks on an ongoing basis. The fiscal year 2022 government-wide total of reported estimated improper payments was $247 billion, but it did not include estimates for some key government programs.
The comprehensive long-term fiscal projections presented in the Statement of Long-Term Fiscal Projections and related information show that based on current revenue and spending policies, the federal government continues to face an unsustainable long-term fiscal path. Since 2017, GAO stated that Congress should develop a fiscal plan to place the federal government on a sustainable fiscal path and ensure that the United States remains in a strong economic position to meet its social and security needs, as well as to preserve flexibility to address unforeseen events like public health emergencies. Additionally, GAO recommended that Congress consider alternative approaches to the current debt limit as part of any long-term fiscal plan.
In commenting on a draft of this report, Department of the Treasury and Office of Management and Budget (OMB) officials expressed their continuing commitment to addressing the problems this report outlines.
Why GAO Did This Study
The Secretary of the Treasury, in coordination with the Director of OMB, is required to annually submit audited financial statements for the U.S. government to the President and Congress. GAO is required to audit these statements. The Government Management Reform Act of 1994 has required such reporting, covering the executive branch of government, beginning with financial statements prepared for fiscal year 1997. The consolidated financial statements include the legislative and judicial branches.
For more information, contact Dawn S. Simpson at (202) 512-3406 or simpsondb@gao.gov or Robert F. Dacey at (202) 512-3406 or daceyr@gao.gov.
