DOD Financial Management: Benefits to Date of Financial Statement Audits and Need to Improve Financial Management Systems
Fast Facts
DOD is working to improve its long-standing financial management issues. Its goal is to get a "clean" audit opinion on its financial statements—indicating that they're presented fairly and consistent with accounting principles.
We testified that DOD's financial audits have led to financial management benefits and more, including identifying assets that DOD didn't even know it had.
DOD is also modernizing its financial IT systems. These efforts move slowly, and challenges continue. But, modernization has helped DOD save at least $5.5 billion by preventing it from making payments that shouldn't have been made between 2020 and 2023.

Highlights
What GAO Found
Several Department of Defense (DOD) components have achieved an unmodified (clean) audit opinion, including most recently the Marine Corps. However, as of fiscal year 2023, DOD remains the only agency to have never received a department-wide clean audit opinion. DOD must overcome challenges related to its financial management systems to achieve this goal.
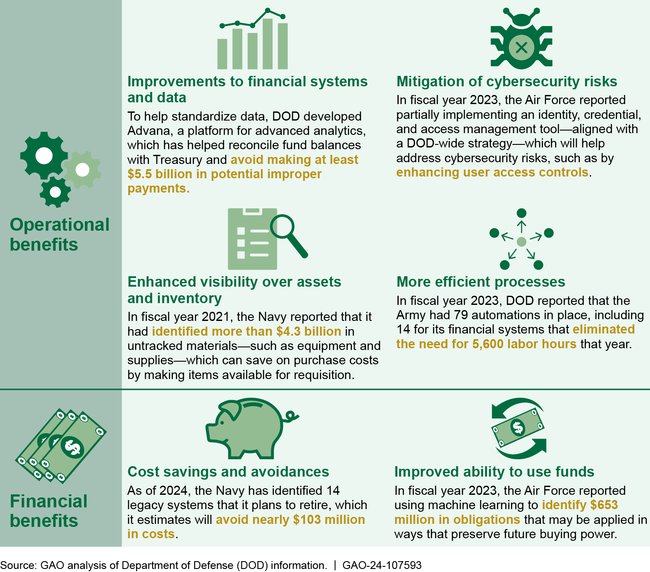
To date, audits have provided valuable insight into improving the organization's financial management and accountability over its resources. According to DOD, audits have resulted in both operational and financial benefits (see figure).
Examples of Operational and Financial Benefits of DOD Financial Statement Audits
To make greater progress DOD needs to take steps to address GAO's 29 open recommendations associated with challenges DOD faces in meeting target remediation dates, addressing auditor-identified deficiencies, improving system transitions, and addressing its planning, oversight, and data limitations. Addressing these recommendations will help DOD track audit remediation efforts, avoid system transition delays, modernize its financial systems, and achieve a clean audit opinion.
Why GAO Did This Study
DOD is responsible for about half of the federal government's discretionary spending and about 15 percent of its total spending. It is important for DOD to obtain a clean audit opinion to demonstrate that its financial statements and underlying financial management information are reliable for decision-making. DOD's financial management and IT systems are both on GAO's High Risk List because of pervasive weaknesses in the agency's business operations, finances, and acquisition management.
To help DOD improve its financial management, DOD's auditors have issued thousands of notices of findings and recommendations and 28 material weaknesses. In response, DOD has identified priority areas and developed a strategy, plans, and roadmaps. These actions are important steps, but DOD has faced challenges in meeting target remediation dates, and DOD's use of aging legacy financial systems continues to hinder its efforts.
This testimony discusses (1) DOD's financial management systems, (2) the financial and operational benefits of audits, and (3) DOD's progress in responding to the deficiencies identified through those audits.
This testimony is based on GAO work from 2020 through 2024 related to DOD's financial management. Details on GAO's methodology can be found in each of the reports cited in this statement.
For more information, contact Asif A. Khan at (202) 512-9869 or khana@gao.gov or Vijay A. D'Souza at (202) 512-7650 or dsouzav@gao.gov.
