Cybersecurity: National Cyber Director Needs to Take Additional Actions to Implement an Effective Strategy
Fast Facts
Cyberattacks threaten federal information systems and the nation's critical infrastructure. The Office of the National Cyber Director leads national cyber policy and strategy.
The Office has a plan to implement the White House's National Cybersecurity Strategy. As of January 2024, the strategy and plan provide a good foundation, but the Office still needs to include more details in the plan to ensure that the strategy can be implemented consistently and effectively government-wide.
Specifically, we recommended that the Office establish performance measures and estimate implementation costs.
Highlights
What GAO Found
The National Cybersecurity Strategy and its implementation plan jointly addressed four of six desirable characteristics identified in prior GAO work and partially addressed the other two (see figure).
Extent to Which the March 2023 National Cybersecurity Strategy and July 2023 Implementation Plan Addressed GAO's Desirable Characteristics of a National Strategy
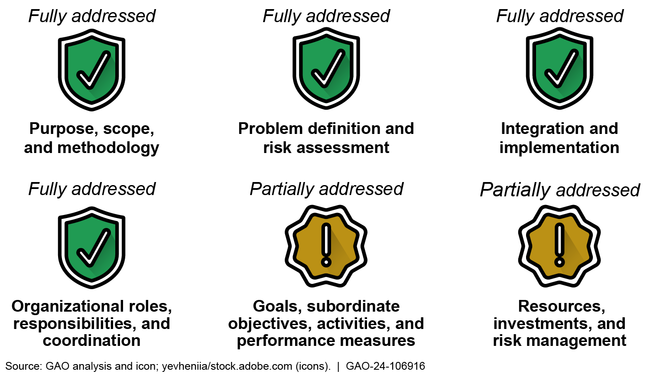
For the partially addressed characteristics, the documents did not fully describe:
- Outcome-oriented performance measures. Office of the National Cyber Director (ONCD) staff said it was not realistic to develop outcome-oriented measures at this point. However, GAO believes it is feasible to develop such measures where applicable. For example, regarding the key initiative of disrupting ransomware attempts, the Department of the Treasury already collects information on the number and dollar value of ransomware-related incidents—for 2021 the reported total dollar value was about $886 million. This demonstrates that developing such measures is feasible and can be used for measuring effectiveness.
- Resources and estimated costs. While the implementation plan outlined initiatives that require executive visibility and interagency coordination, it did not identify how much it will cost to implement the initiatives. ONCD staff said estimating the cost to implement the entire strategy was unrealistic. However, while certain initiatives may not warrant a specific cost estimate, other activities supporting some of the key initiatives with potentially significant costs justify the development of a cost estimate. Such cost estimates are essential to effectively managing programs. Without such information, uncertainty can emerge about investing in programs.
Without actions to address these shortcomings, ONCD will likely lack information on plan outcomes and encounter uncertainty on funding of activities.
Why GAO Did This Study
For over 25 years GAO has identified cybersecurity as a high-risk area. During this period, the threat of cyber-based intrusions and attacks on IT systems by malicious actors has continued to grow.
A national strategy to guide the government's cybersecurity activities is needed to address this threat. Recognizing the need for national cybersecurity leadership, Congress established ONCD to support the nation's cybersecurity and lead the development of a national strategy. In March 2023, the White House issued the National Cybersecurity Strategy to outline how the administration will manage the nation's cybersecurity. In July 2023, ONCD issued an implementation plan defining how the strategy will be executed.
GAO's objective was to examine the extent to which the National Cybersecurity Strategy and implementation plan addressed desirable characteristics of a national strategy. To do so, GAO assessed relevant documents and other evidence against desirable characteristics of a national strategy. GAO also interviewed ONCD staff.
Recommendations
GAO is making two recommendations to ONCD to develop outcome-oriented measures and estimate costs of implementation activities. ONCD agreed with GAO's recommendation on outcome-oriented measures but disagreed with the recommendation on estimating costs. GAO continues to believe that ONCD should assess the plan's initiatives to identify those that warrant a cost estimate and develop such cost estimates.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Office of the National Cyber Director | The Director of ONCD should work with relevant federal entities to assess the initiatives that lend themselves to outcome-oriented performance measures and develop such performance measures for those initiatives in a timely manner to gauge effectiveness in meeting the goals and objectives of the National Cybersecurity Strategy. (Recommendation 1) |
ONCD agreed with this recommendation and said it will assess the initiatives to identify those that warrant outcome-oriented performance measures. When we confirm what actions ONCD has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Office of the National Cyber Director | The Director of ONCD should work with relevant federal entities to assess the initiatives to identify those that warrant a cost estimate and develop such cost estimates. (Recommendation 2) |
ONCD disagreed with this recommendation. We continue to believe that the recommendation is valid because we identified initiatives that may require significant costs. As such, we will monitor ONCD's efforts to address this recommendation.
|
