Ukraine: U.S. Agencies Should Improve Tracking of Authorized U.S.-Origin Defense Article Transfers Requested by Foreign Donors
Fast Facts
At least 30 countries have pledged over $148 billion in security assistance to Ukraine since Russia's invasion in 2022. This includes $2 billion worth of defense items of U.S. origin—such as missiles and ammunition—that foreign donors requested to transfer to Ukraine.
The State Department approves these transfers, and the Defense Department is required to monitor the items.
However, State hasn't consistently shared approval information with DOD and neither DOD nor State verify the delivery of these transfers. DOD can't effectively monitor these items. We recommended ways to improve information sharing and monitoring.

Highlights
What GAO Found
The U.S. and more than thirty international donors have provided security assistance to the government of Ukraine in response to Russia's full-scale invasion in February 2022. Among international donors, 25 European countries collectively pledged over $73 billion in security assistance to Ukraine as of April 30, 2024. For many of these countries, the pledges are equivalent to a significant percentage of their GDP and defense budgets.
The Departments of Defense (DOD) and State (State) have coordinated within the U.S. government and with foreign donors to develop and execute donation strategies to collectively address Ukraine's needs. The agencies generally facilitate international donations of defense articles in three ways: 1) authorizing foreign donors to transfer U.S.-origin defense articles to Ukraine; 2) providing logistical support services, such as equipment delivery and maintenance; and 3) incentivizing donations by providing foreign military financing (FMF) to replenish defense articles donated to Ukraine. Of the $72 billion of U.S. security assistance, $6.33 billion is obligated for FMF. State has allocated FMF to 10 European countries that pledged security assistance to Ukraine.
U.S. Roles in Foreign Donations of Defense Articles to Ukraine
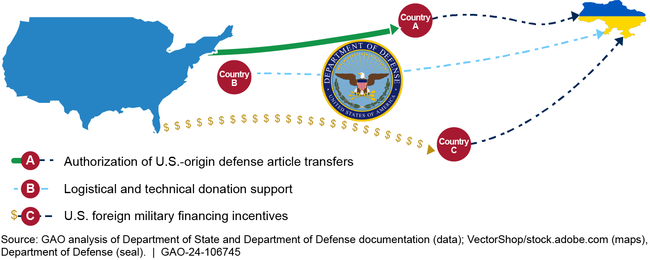
State had authorized 217 third party transfers (TPT) of U.S.-origin defense articles by over 26 foreign donors to Ukraine as of April 2024. DOD is required to conduct end-use monitoring on these defense articles; however, DOD is limited in its ability to do so. GAO found that State and DOD's inconsistent communication of authorized TPT details makes it difficult for DOD to track them. DOD officials are often unaware of TPTs authorized by State until they are identified upon entry to Ukraine, if at all. State has taken some steps to enhance its document management system for TPTs to improve external information sharing. However, neither State nor DOD verifies the delivery of authorized TPTs to Ukraine. State does not consistently request TPT delivery notification from donors, and its policy does not require it. DOD officials acknowledge that records of authorized TPTs transferred to Ukraine, including those subject to enhanced end-use monitoring, are inaccurate. Timely and complete information about authorized TPTs to Ukraine would help ensure that DOD can properly account for sensitive defense articles and better prevent misuse and diversion.
Why GAO Did This Study
The U.S. has been a leading provider of security assistance to Ukraine. As of April 2024, Congress has appropriated more than $174 billion for Ukraine assistance, of which $72 billion is specifically for security assistance. The amount and speed of assistance distributed has raised questions about the need to monitor and ensure accountability for the defense articles provided.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023 included a provision for GAO to perform additional oversight over U.S. efforts to assist Ukraine. GAO's review examines (1) information on the security assistance donations made by the U.S. and foreign countries, (2) how U.S. agencies coordinate with foreign donors to provide defense articles to Ukraine and key factors considered, and (3) how State authorizes third party transfers and to what extent U.S. agencies conduct end-use monitoring of transferred articles.
GAO analyzed agency documentation; met with DOD and State officials in the U.S., Germany, and Poland; and assessed State, DOD, and public data on defense articles donated to Ukraine from January 2022 to April 2024.
Recommendations
GAO is making six recommendations to State and DOD. Four identify steps the agencies should take to collect delivery information from foreign donors for TPTs and incentivized donations, and two are related to steps State should take to improve information sharing about TPTs subject to U.S. end-use monitoring. State concurred with five recommendations and DOD partially concurred with one.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of State | The Secretary of State should require the Bureau of Political Military Affairs to request that divesting countries notify appropriate officials within U.S. Embassies' Offices of Defense Cooperation of donation deliveries to Ukraine when those donations were a condition of FMF assistance to the divesting country. (Recommendation 1) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of State | The Secretary of State should ensure that RSAT take steps to consistently share TPT authorizations with Security Cooperation Offices for divesting and recipient countries. (Recommendation 2) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of State | The Secretary of State should instruct RSAT to further strengthen its document management system for authorizations of TPTs, and implement processes outlined in its standard operating procedures to improve its ability to share information with other U.S. agencies. (Recommendation 3) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of State | The Secretary of State should take steps to ensure that RSAT's TPT authorizations include a request for divesting countries to notify DSCA and Security Cooperation Offices of related defense article deliveries. (Recommendation 4) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of State | The Secretary of State should require RSAT to request that divesting governments that have received TPT authorizations from January 2022 to July 2024 notify DSCA and Security Cooperation Offices of related defense article deliveries to Ukraine. (Recommendation 5) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should establish a formal process to verify deliveries of defense articles provided through authorized TPTs and ensure SCIP is updated as appropriate. (Recommendation 6) |
When we confirm what actions the agency has taken in response to this recommendation, we will provide updated information.
|
