Artificial Intelligence: Fully Implementing Key Practices Could Help DHS Ensure Responsible Use for Cybersecurity
Fast Facts
While responsible use of artificial intelligence can improve security, irresponsible use may pose risks. We looked at what the Department of Homeland Security is doing to ensure responsible use of its AI for cybersecurity.
DHS created a public inventory of "AI use cases"—how it uses AI. But DHS doesn't verify whether each case is correctly characterized as AI. Of the 2 cybersecurity cases in the inventory, we found 1 isn't AI.
DHS also hasn't ensured that the data used to develop the AI use case we assessed is reliable—which is an accountability practice in our AI framework.
Our recommendations address these and other issues.
Highlights
What GAO Found
To promote transparency and inform the public about how artificial intelligence (AI) is being used, federal agencies are required by Executive Order No. 13960 to maintain an inventory of AI use cases. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has established such an inventory, which is posted on the Department's website.
However, DHS's inventory of AI systems for cybersecurity is not accurate. Specifically, the inventory identified two AI cybersecurity use cases, but officials told us one of these two was incorrectly characterized as AI. Although DHS has a process to review use cases before they are added to the AI inventory, the agency acknowledges that it does not confirm whether uses are correctly characterized as AI. Until it expands its process to include such determinations, DHS will be unable to ensure accurate use case reporting.
DHS has implemented some but not all of the key practices from GAO's AI Accountability Framework for managing and overseeing its use of AI for cybersecurity. GAO assessed the one remaining cybersecurity use case known as Automated Personally Identifiable Information (PII) Detection—against 11 AI practices selected from the Framework (see figure).
Status of the Department of Homeland Security's Implementation of Selected Key Practices to Manage and Oversee Artificial Intelligence for Cybersecurity
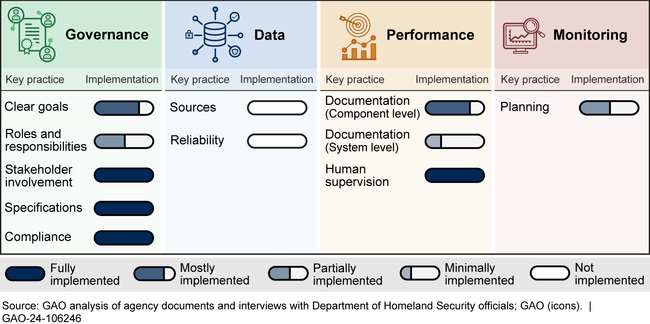
GAO found that DHS fully implemented four of the 11 key practices and implemented five others to varying degrees in the areas of governance, performance, and monitoring. It did not implement two practices: documenting the sources and origins of data used to develop the PII detection capabilities, and assessing the reliability of data, according to officials. GAO's AI Framework calls for management to provide reasonable assurance of the quality, reliability, and representativeness of the data used in the application, from its development through operation and maintenance. Addressing data sources and reliability is essential to model accuracy. Fully implementing the key practices can help DHS ensure accountable and responsible use of AI.
Why GAO Did This Study
Executive Order No. 14110, issued in October 2023, notes that while responsible AI use has the potential to help solve urgent challenges and make the world more secure, irresponsible use could exacerbate societal harms and pose risks to national security. Consistent with requirements of Executive Order No. 13960, issued in 2020, DHS has maintained an inventory of its AI use cases since 2022.
This report examines the extent to which DHS (1) verified the accuracy of its inventory of AI systems for cybersecurity and (2) incorporated selected practices from GAO's AI Accountability Framework to manage and oversee its use of AI for cybersecurity.
GAO reviewed relevant laws, OMB guidance, and agency documents, and interviewed DHS officials. GAO applied 11 key practices from the Framework to DHS's AI cybersecurity use case—Automated PII Detection. DHS uses this tool to prevent unnecessary sharing of PII. GAO selected the 11 key practices to reflect all four Framework principles, align with early stages of AI adoption, and be highly relevant to the specific use case.
Recommendations
GAO is making eight recommendations to DHS, including that it (1) expand its review process to include steps to verify the accuracy of its AI inventory submissions, and (2) fully implement key AI Framework practices such as documenting sources and ensuring the reliability of the data used. DHS concurred with the eight recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Chief Technology Officer should expand its review process to include steps to verify the accuracy of its AI inventory submissions. (Recommendation 1) |
In October 2024, DHS developed guidance for its AI Use Case Inventory that describes an expanded review process. The guidance identifies roles and responsibilities for compiling and reviewing inventories from DHS components. For example, an inventory manager in each component is responsible for ensuring the accuracy of use cases reported for the inventory. This individual is also responsible for consulting with senior AI officials and officials with technical and operational knowledge of each use case to determine whether a use case should be added to the inventory. According to the guidance, the DHS Inventory Lead reviews inventory submissions for completeness and accuracy to provide oversight on behalf of the Chief Technology Officer.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should develop metrics to consistently measure progress toward all stated goals and objectives for Automated PII Detection. (Recommendation 2) |
In September 2024, in response to this recommendation, CISA developed metrics to assess progress toward the goals of more reliably, accurately, and efficiently processing of data pertaining to personally identifying information (PII) for the Automated PII Detection component. Metrics include the number of PII detections, the rate of false detections, and the time from detection to dissemination, among others. These metrics are presented in a dashboard user interface for analysts to monitor monthly.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should clearly define the roles and responsibilities and delegation of authority of all relevant stakeholders involved in managing and overseeing the implementation of the Automated PII Detection component to ensure effective operations and sustained oversight. (Recommendation 3) |
In January 2025, CISA's Cybersecurity Division (CSD), Mission Engineering subdivision (ME) developed a document that defines the roles and responsibilities of relevant stakeholders involved in managing and overseeing the implementation of the Automated Personally Identifiable Information (PII) Detection component. For example, CISA's Office of Privacy, Access, Civil Liberties and Transparency is identified as a stakeholder responsible for conducting biannual privacy oversight reviews to ensure the system is operating as intended to monitor CISA's cybersecurity division's compliance with the handling of personal information.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should document the sources and origins of data used to develop the Automated PII Detection component. (Recommendation 4) |
In January 2025, CISA's Cybersecurity Division (CSD), Mission Engineering subdivision (ME) developed a design and specifications document, which documents the sources and origins of the data for the Automated PII Detection component. The document describes the flow of cyber threat intelligence from external partners, who submit the data to CISA in the specific format that enables the Automated PII Detection to read it.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should take steps to assess and document the reliability of data used to enhance the representativeness, quality, and accuracy of the Automated PII Detection component. (Recommendation 5) |
As of January 2025, CISA's Cybersecurity Division (CSD), Mission Engineering subdivision (ME) had taken some actions toward addressing this recommendation. CISA CSD ME developed an assessment report to evaluate the results of the Automated PII Detection component. In the report, reliability assessments of the quality and accuracy of data are documented. For example, data were reviewed for metrics such as time from detection to dissemination and rates of false detection. To fully address this recommendation, CISA should also describe how it assesses the reliability of data used to enhance representativeness. As of April 2025, we are following up with the agency to obtain additional information.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should document its process for optimizing the elements used within the Automated PII Detection component. (Recommendation 6) |
In December 2024, in response to this recommendation, CISA documented its standard operating procedures for optimizing the Automated PII Detection component. The procedures define tasks to support system performance monitoring and improvement. Included among these tasks are those related to configuration, system resource utilization, and enhancements to optimize the Automated PII Detection service.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should document its methods for testing performance including limitations, and corrective actions taken to minimize undesired effects of the Automated PII Detection component to ensure transparency about the system's performance. (Recommendation 7) |
In October 2024, in response to this recommendation, CISA developed standard operating procedures for testing related to the Automated PII Detection component. These procedures document human review actions and functional testing steps that address limitations and corrective actions. For example, CISA's Cybersecurity Division (CSD), Mission Engineering subdivision (ME) notes that the application's reliance on human review is a limitation. The procedures identify steps for the functional testing team to take including to validate that PII was detected and to identify and resolve any performance failure.
|
| Department of Homeland Security | The Director of CISA should establish specific procedures and frequencies to monitor the Automated PII Detection component to ensure it performs as intended. (Recommendation 8) |
In December 2024, in response to this recommendation, CISA developed a monitoring plan for the Automated Indicator Sharing 2.0 Personally Identifiable Information Detection System. The plan includes procedures and frequencies for monitoring the Automated PII Detection component. The procedures include manual and automatic testing to ensure the component operates as intended.
|
