The Decentralized Structure of the Federal Reserve System
This week, a key component of the Federal Reserve System—the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)—will meet to review U.S. economic and financial conditions and determine monetary policy.
In today’s WatchBlog, we explore how the Federal Reserve System is structured and why.
What is the Federal Reserve System?
The Federal Reserve System—or, “the Fed”—is the country’s central bank.
Its unique public-private organization includes:
- the Board of Governors—an independent federal agency
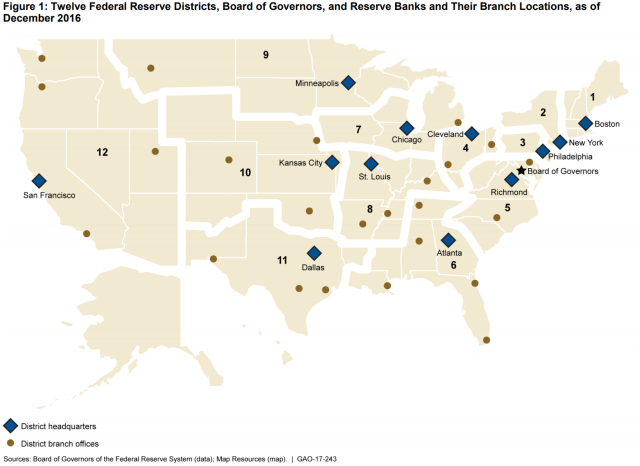
- 12 regional Reserve Banks—private corporations acting as fiscal agents of the government
- the FOMC—a committee comprising Reserve Bank presidents and members of the Board of Governors
Reserve Banks operate the System
The Fed is divided into 12 districts, with each district served by a regional Reserve Bank. Reserve Banks are the operating arms of the Fed. They:
- distribute currency and coins
- provide short-term loans to banks
- supervise banks
- provide educational information on consumer protection rights and laws
Reserve Banks aren’t federal agencies—they’re individually incorporated. Each has a board of directors and stockholders from commercial banks operating within their district. In most cases, each regional Reserve Bank also operates one or more branch offices.
The Board manages the System
The Board of Governors’ main goal is to monitor and promote the stability of financial markets. Among other things, it supervises Reserve Banks and sets the interest rate commercial banks are charged on loans from their regional Reserve Banks. It also submits reports to and testifies before Congress about monetary policy decisions and economic prospects for the future.
The Board, located in Washington, D.C., is led by 7 members who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
FOMC directs open market operations
FOMC influences the total amount of money and credit available in the economy by purchasing or selling securities in the secondary market on behalf of the Fed. FOMC consists of the 7 members of the Board of Governors, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York president, and 4 other Reserve Bank presidents who serve on a rotating basis.
Why is the Federal Reserve System structured this way?
The Fed was designed as a decentralized independent agency to ensure that monetary policy decisions would be representative of all regions of the country and free from political influence. Research shows that countries with high central bank independence usually maintain lower levels of inflation.
The Fed’s monetary policy decisions don’t have to be approved by the President, the executive branch of the government, or Congress. However, the Fed is subject to oversight by Congress and is required to conduct monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
Check out our full report for more information on the Fed.
- Comments on GAO’s WatchBlog? Contact blog@gao.gov.
GAO Contacts
Related Products

GAO's mission is to provide Congress with fact-based, nonpartisan information that can help improve federal government performance and ensure accountability for the benefit of the American people. GAO launched its WatchBlog in January, 2014, as part of its continuing effort to reach its audiences—Congress and the American people—where they are currently looking for information.
The blog format allows GAO to provide a little more context about its work than it can offer on its other social media platforms. Posts will tie GAO work to current events and the news; show how GAO’s work is affecting agencies or legislation; highlight reports, testimonies, and issue areas where GAO does work; and provide information about GAO itself, among other things.
Please send any feedback on GAO's WatchBlog to blog@gao.gov.