Nuclear Security Enterprise: NNSA Should Use Portfolio Management Leading Practices to Support Modernization Efforts
Fast Facts
The National Nuclear Security Administration is spending billions on programs to modernize the nation's nuclear weapons stockpile.
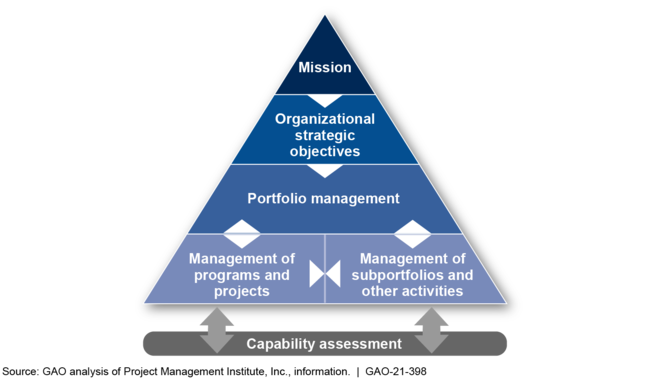
Managing expensive, complex programs is challenging. Industry leaders use portfolio management to prioritize resources for programs that best achieve an organization's strategic goals.
NNSA says that its Weapons Activities work is a portfolio and has partially implemented leading practices. However, the agency hasn't clearly defined this portfolio—i.e., fully documented what's included in the portfolio and how it links to the agency's mission and strategic objectives. We recommended that it do so.
A model of the B61-12 nuclear bomb

Highlights
What GAO Found
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has partially implemented selected leading practices to manage the work necessary to maintain and modernize the nation's nuclear weapons stockpile. GAO found that NNSA is in the early stages of initiating its portfolio management processes and has partially implemented leading practices, such as establishing a clearly defined portfolio of work. For example, NNSA officials stated that its Weapons Activities appropriations account is a portfolio of work. However, NNSA has not developed clearly defined and appropriately empowered governance roles, such as a portfolio manager, for its Weapons Activities portfolio. As NNSA continues to develop its approach to portfolio management, establishing a portfolio management framework—consistent with selected leading practices—may allow NNSA to fully implement all leading practices, better define how program offices will pursue strategic stockpile modernization objectives, and optimize portfolio performance in the event that budget trade-offs become necessary.
NNSA's offices have undertaken four separate efforts to identify and assess the capabilities needed across the nuclear security enterprise to meet its stockpile maintenance and modernization mission, but NNSA has not developed a comprehensive or complete capability assessment that could support its portfolio management approach (see fig.). NNSA undertook three of these four independent efforts to identify and assess capabilities in response to different legislative direction and did not incorporate information on all elements of a capability (knowledge, human capital, and infrastructure) in any of the individual efforts. Working across the agency to conduct a comprehensive, complete capability assessment would provide NNSA with a portfolio-level view of the enterprise's capabilities and needs, allowing for planning that considers interdependencies that have been missed in the past when planning focused on individual programs or projects.
Relationship between Capability Assessment and Portfolio Management
Why GAO Did This Study
NNSA is simultaneously modernizing the nation's nuclear weapons stockpile and the infrastructure on which weapons research and production programs depend. These efforts include multi-billion-dollar defense programs and projects that provide the capabilities needed for maintenance and modernization programs. Congress previously directed NNSA to identify its needed capabilities.
The Senate report accompanying the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 includes a provision for GAO to review NNSA's approach to managing its defense programs and to identifying capabilities. This report examines the extent to which NNSA (1) used selected portfolio management leading practices to manage its maintenance and modernization programs and projects and (2) developed a comprehensive and complete capability assessment to support portfolio management.
GAO reviewed NNSA documentation related to portfolio management and capabilities and compared it with leading practices and legislative requirements. GAO also interviewed NNSA officials from six agency offices.
Recommendations
GAO is making two recommendations: NNSA should (1) establish a portfolio management framework and (2) develop a comprehensive and complete capability assessment. NNSA concurred in principle with the recommendations and stated that they have addressed them. GAO believes that NNSA needs to take additional actions to fully address the recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| National Nuclear Security Administration |
Priority Rec.
The NNSA Administrator should establish an enterprise-wide portfolio management framework. The framework should define the portfolio of weapons stockpile and infrastructure maintenance and modernization programs and its governance roles, as well as include portfolio-level selection criteria, prioritization criteria, and performance metrics. (Recommendation 1) |
Open – Partially Addressed
NNSA agreed in principle with our recommendation to establish an enterprise-wide portfolio management framework. In its comments on our recommendation, NNSA recognized that it is in the early stages of implementing portfolio management processes for its Weapons Activities portfolio of work and that the leading practices we identified can be useful in developing a portfolio management approach. In a June 2021 advanced change directive on the planning, programming, budgeting, and evaluation (PPBE) process, NNSA established that PPBE Account Integrator positions are responsible for integrating and prioritizing their portfolio--Weapons Activities being one of those. In the fiscal year 2022 Stockpile Stewardship and Management Plan (SSMP), NNSA added a section on portfolio management. The fiscal year 2022 SSMP states that NNSA considers the Weapons Activities budget account a portfolio of work that is managed by its programs and underpinned by specific capabilities. In response to Congressional direction included in the Joint Explanatory Statement to Accompany the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2022, NNSA provided a briefing in November 2022 on its progress addressing our recommendation. In the briefing materials, NNSA provided a Weapons Activities portfolio structure that generally aligns with the Weapons Activities budget structure and includes scopes of work managed by NNSA's Office of Defense Programs, Office of Infrastructure, Office of Defense Nuclear Security, and Office of Information Management. NNSA's next steps include establishing the portfolio management process and formalizing the process in updated strategic documents. In January 2023, NNSA estimated that this would take about 2 years--by January 2025. We are encouraged that NNSA has taken action. We continue to believe that an established portfolio management framework--a cohesive, strategic document that clearly describes how to manage the portfolio and how to assess its overall performance--would provide NNSA with a more structured and defensible approach to managing the billions of dollars of work that comprise the Weapons Activities portfolio. We will continue to review NNSA's progress to address this recommendation.
|
| National Nuclear Security Administration | The NNSA Administrator should work across the agency's offices that contribute to achieving the goals and objectives of the stockpile maintenance and modernization portfolio to develop a comprehensive capability assessment that incorporates the three elements of capabilities (knowledge, human capital, and infrastructure). (Recommendation 2) |
Open – Partially Addressed
NNSA agreed in principle with our recommendation to work across offices to develop a comprehensive and complete capability assessment. However, NNSA stated that it considered the recommendation to be closed--that sufficient action has already been taken to address the recommendation. In its comments on our report, NNSA referenced the fiscal years 2020 and 2021 Stockpile Stewardship and Management Plan (SSMP); however, we found that NNSA's efforts to identify and assess capabilities in these two years' plans did not fully consider all three elements of a capability (knowledge, human capital, and infrastructure). NNSA released its fiscal year 2022 SSMP in March 2022, which more clearly presented NNSA's separate efforts in a comprehensive way. This full version included or specifically referenced all of the capabilities that NNSA needs for the enterprise to meet its nuclear weapons mission that the agency described in the other efforts. NNSA released its fiscal year 2023 SSMP--a biennial summary version--in April 2023 and its fiscal year 2024 SSMP--the full version--in November 2023. These plans further refined how NNSA describes necessary capabilities and integrates information from its previous efforts to assess capabilities. Although the more recent SSMPs clearly link infrastructure with each capability, the plans do not include an assessment of how many federal staff and their specific competencies that are needed to support each capability. We believe that actions to clearly identify (1) the federal competencies needed to conduct work, and (2) the federal workforce conducting work would better support NNSA's strategic management of the Weapons Activities portfolio. We will continue to review NNSA's progress to address this recommendation.
|
